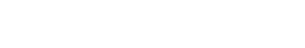If you have a product idea and want to bring it to life, you should understand that it isn’t a straight line. It should pass through several stages before reaching the market. Let’s carefully look into the prototyping stage and turn your idea into reality together.
Using prototyping services before production can offer a range of benefits for businesses. It allows companies to take a proactive approach when developing products and services that correspond to customer needs, testing and refining them before they are publicly available. Thus, you can start production with greater confidence and accuracy in your design decisions – minimizing costly mistakes and optimizing the product that will likely succeed in the market.
Besides, it is hugely beneficial when minimizing change requests during the development stage. Potential issues can be identified and addressed early in the development cycle, contributing to the product’s timely delivery.
Therefore, we usually recommend that our clients follow the so-called test-and-learn approach to gain insights into the product’s user experience and functionality, define pitfalls, form a better vision of the product, and see in what direction to move.
Prototyping – Product Discovery Phase Services
Before starting product development, Quintagroup offers Discovery Phase services. This includes iterative meetings with an Architect, Project Manager, UI/UX expert, Business Analyst, and stakeholder representative to collect and evaluate all relevant information. The outcome of this session is usually an offer that may also contain the LF prototypes of the product, scope of work, information on pricing, and solution architecture.
The discovery phase may last from a couple of days to a couple of weeks, depending on the complexity of the project and its objectives. However, it can also include Sprint 0. From there, detailed prototyping can be done in subsequent sprints to obtain a fully clickable prototype that users can test and finalize based on feedback.
By carefully assessing user needs beforehand, Quintagroup can create practical and easy-to-use products while providing maximum value to customers.
Prototyping as a part of the Design Thinking process
Design thinking is a methodology used to tackle design problems in an iterative, human-centered way. At its core, Design Thinking consists of five stages:
- Define
- Research
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
Prototyping is crucial in the process, as it allows for exploring possibilities and helps refine the concept. It also serves as a means of communication with other stakeholders, who provide feedback and influence product development.
When done correctly, prototyping is an invaluable tool that efficiently turns ideas into desired products. It encourages experimentation and provides tangible results that can be tested further to determine if the project is on the right track. In addition, it enables designers to think outside the box and quickly evaluate alternative solutions before sending them off for production.
This can be applied to developing web solutions and various product types. Designers create digital models and prototypes using virtual reality or other simulation tools to ensure a smooth integration process with existing systems and technologies.
What is Prototyping in Software Engineering?
Like any other industry, prototyping in a digital world stands for the initial version of the product you will launch. Prototypes are meant to be simple, not detailed; this makes them more accessible for developers to change and improve as necessary.
The general idea of prototyping is to create an incomplete product to:
- Check whether a visual design of the application under development complies with stakeholders’ requirements; conduct usability testing and ensure that graphic elements and content require no adjustments or changes. Such prototypes are also known as high-fidelity prototypes, and they include all the visual features, content, and capabilities of the final product;
- Carry out functionality testing. This one is called a low-fidelity prototype and includes only key UI elements and specific pieces of content.
4 Types of Prototyping
- Rapid Prototyping
The very name of the type speaks for itself. Rapid prototyping aims to make quick changes and improvements to the design and its functionality. “Rapid” means that the team makes short iterations only to core elements that have the most significant impact on the final version of the product.
- Incremental model
Incremental prototyping implies that a team works together collaboratively while developing an initial draft; multiple iterations will be created from the initial prototype as new features or changes emerge from testing and feedback from stakeholders or users.
- Evolutionary Prototyping
In this approach, simple versions of the prototype are made incrementally over time as needed until all elements have been incorporated into a complete prototype. It differs from the incremental model, as each new version requires repeating a particular cycle of activities.
- Extreme Prototyping
This method entails creating three separate versions – an interface skeleton, data design layer, and server component – which must communicate accurately with one another for proper functioning before any coding is done for actual use cases.
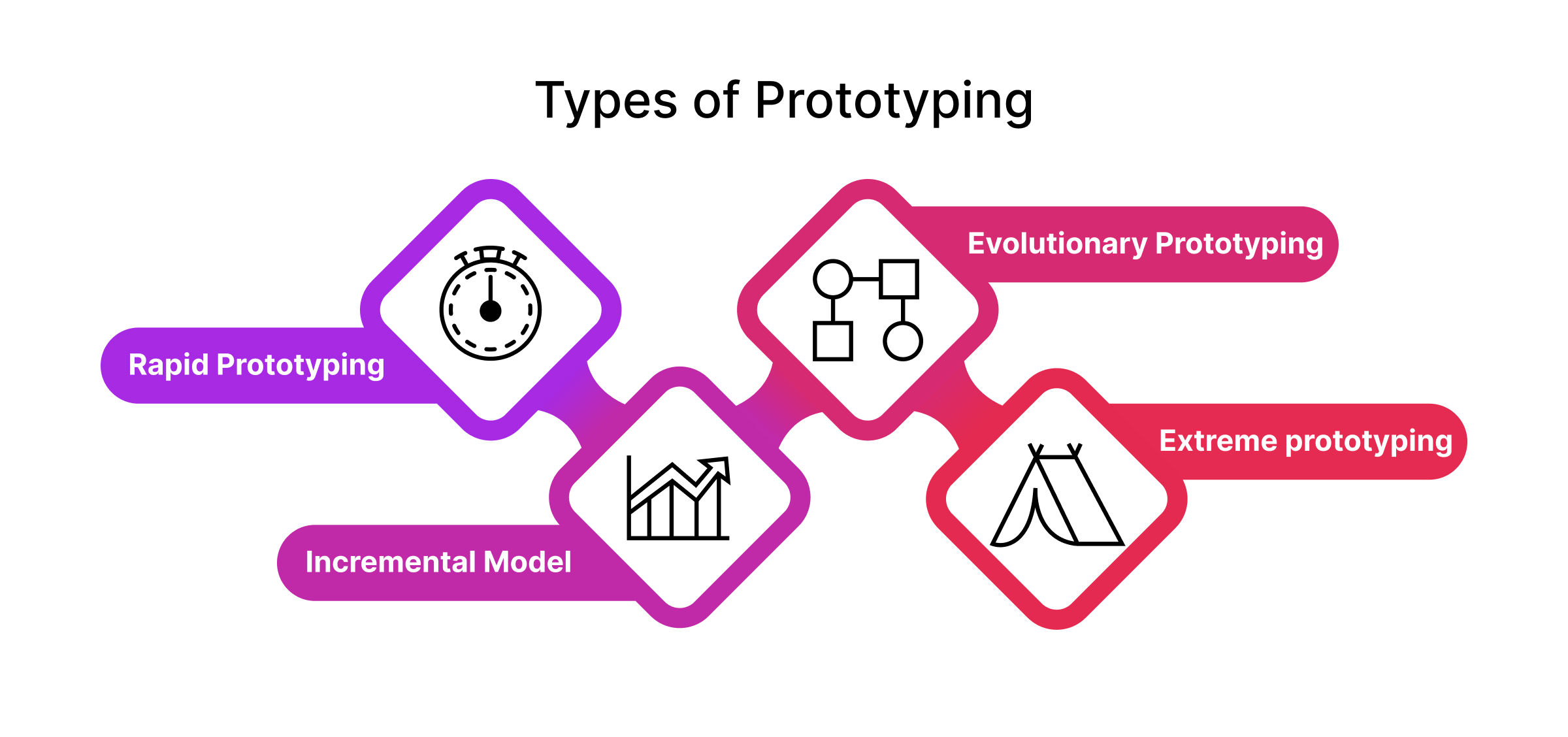
The Process of Prototyping
When prototyping an application, five stages are involved in executing it properly.
- Define core requirement: before any coding takes place, stakeholders should identify what features their application should have and who its intended users will be. From here on, they can determine how best to meet their needs through design and functionality.
- Initial prototype development: once requirements have been outlined, a BA specialist or UX expert will create a basic version featuring those core components – referred to as wireframes or storyboards – where they test elements related to aesthetics and usability rather than actual functionalities at this stage.
- Test and review the prototype: our specialists go through each stage, step by step, checking the prototype for inconsistencies. Feedback from stakeholders also factors heavily into determining whether any additional adjustments need to be made during this stage.
- Implement changes and improve the prototype: as mentioned above, based on the feedback, there may be certain areas requiring improvements.
- Finalize the prototype: ensure the performance is optimized and the code runs smoothly. Once all desired changes are implemented successfully, the prototype is ready for development.
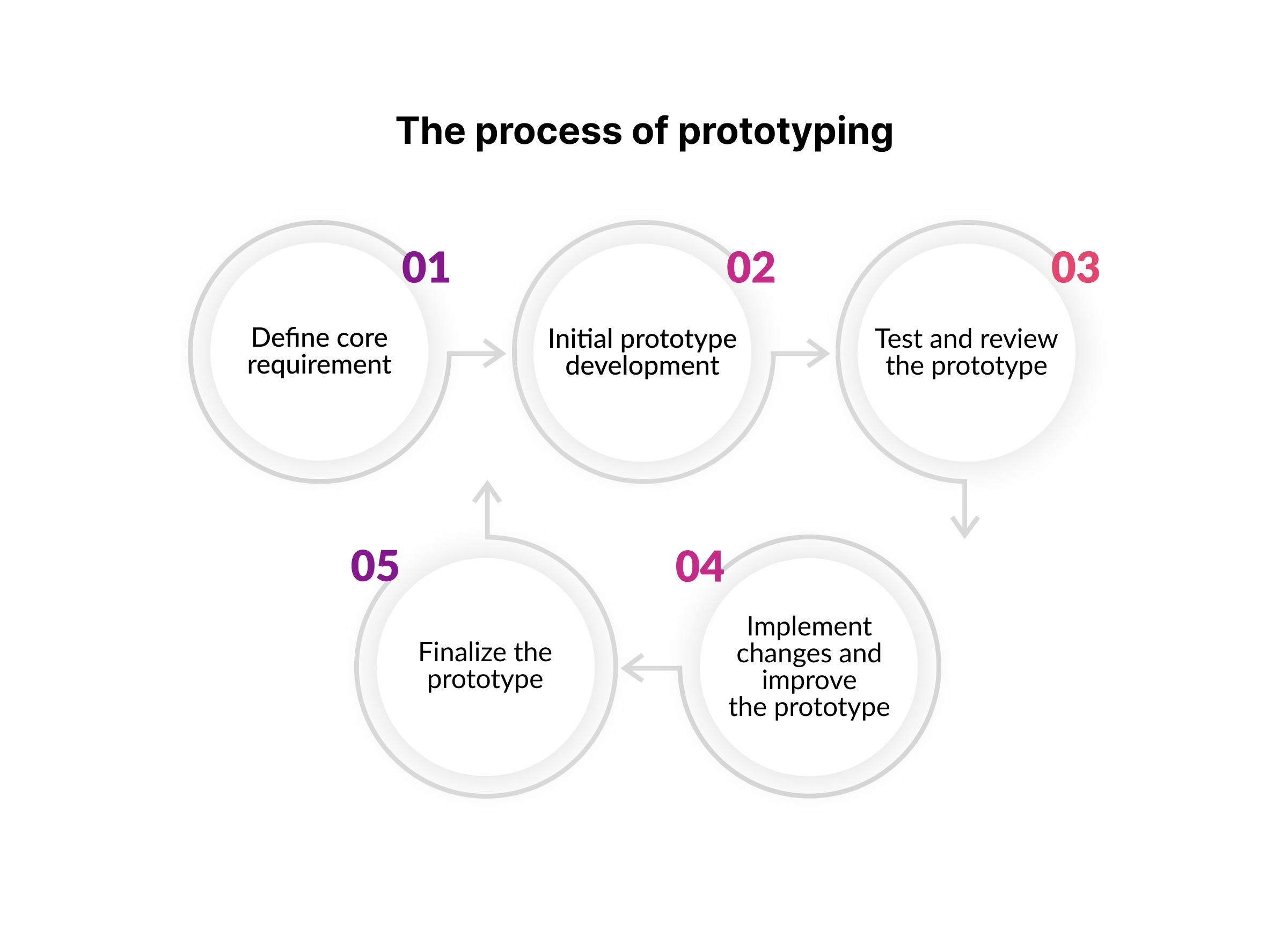
Why is Software Prototyping Important?
Software prototyping plays an essential role in the software development life cycle by helping teams develop applications that meet user requirements without wasting time or resources on building something unnecessary due to inefficient communication.
- It enables developers to test the usability of the software app early on to identify any potential errors before they become costly problems later on.
- It saves time, energy, and money by avoiding costly mistakes because of a lack of understanding of user expectations or miscommunication.
- It allows for a more streamlined development process as adjustments can be made quickly and easily without starting from scratch if necessary.
- It encourages team collaboration and allows developers to test different areas of an application before launch.
- It gives users a hands-on experience with an unfinished product so they can provide feedback and suggestions, which helps teams create a better final version.
Who Creates Product Prototypes?
It depends on the project requirement and its complexity. The key players are Business Analysts(BA) and User Interface/User Experience(UI/UX) experts. BAs are responsible for understanding customer needs, gathering data, and bridging the gap between the client and the development team. UI/UX professionals use their creative skills to provide efficient interfaces and excellent user experience.
Tools We Use for Prototyping
As you already know, software prototyping is necessary to ensure successful product development and deployment. Several tools are available to assist in this process, including Figma, Balsamiq, and InVision.
Figma is a collaborative interface design tool that can be used to build wireframes, prototypes, and designs.
Balsamiq has a drag-and-drop interface for creating mockups quickly. This one is used more often by BAs.
InVision provides high-fidelity testing on desktop, mobile, and tablet versions of prototypes before they are launched into the production environment.
These three tools enable development teams to speed up their workflow while producing high-quality apps.
Will I Get All of The Prototypes During the Discovery Stage?
A complex project will require multiple rounds of prototypes during the discovery stage to capture all its nuances, while a simpler one may only need one or two. Additionally, a more extended discovery period will likely result in more prototypes being generated as details are refined, and feedback is incorporated. Ultimately, it’s best to consult with the development team about what you can expect from the prototyping phase for your project.
Ready to Turn Your Ideas Into Reality?
Quintagroup has extensive experience in helping to bring innovative software development projects to life through prototyping. We provide the resources and expertise needed to turn ideas into effective solutions, from preliminary designs and user interface mockups to full-scale interactive prototypes. If you are looking for a partner who can provide hands-on help within an optimal timeframe, get in touch with us.