The IoT is going to connect the world. That’s how it’s stated in the introduction video of the LoRa Alliance, an association devoted to the large scale deployment of LPWAN through the placing in service the LoRaWAN open standard.
The toolkit of Internet of Things has extended with one more possibility. The Wireless Broadband Alliance (WBA) and the LoRa Alliance issued a white paper that mentions a set of new IoT use cases. The use cases are based on merging Wi-Fi and LoRaWAN connectivity technologies.
Wi-Fi & LoRaWAN Deployment Synergies: Expanding Addressable Use Cases For The Internet of Things compares business opportunities of two technologies in separate usage with their combination in different market segments.
According to Tiago Rodrigues, general manager of WBA:
“Wi-Fi and LoRaWAN are two important technologies utilizing the unlicensed spectrum, and they already address a large proportion of IoT use cases. The Deployment Synergies paper highlights the ways in which these technologies are impacting private-public business models and enabling IoT services, while also identifying ways in which the technologies complement one another and can be used to further expand the internet of things.”
If you still have never encountered these two notions here’s a brief explanation.
The difference between LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi
LoRa/LoRaWAN technology
The specification of LoRaWAN lies in a Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) network. It was designed to connect a ‘thing’ - physical object that has a unique identifier, an embedded system and the ability to transfer data over the network - to the internet without wires in regional, national or global networks, and targets key Internet of Things (IoT) requirements such as bi-directional communication, end-to-end security, mobility and localization services.
Wi-Fi technology
Wi-Fi is a class of radio technologies generally exploiting wireless local area networking (WLAN) of devices. It is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi uses multiple parts of the IEEE 802 protocol family and is meant to seamlessly interlink with the wired protocol Ethernet.
Desktop and laptop computers, printers, smart TVs, smartphones and tablets, digital cameras, cars and drones are the devices that may use Wi-Fi networks to connect each other through a wireless Access Point as well as to connected Ethernet devices. The range of an access point (or hotspot) is about 20 meters indoors and a larger range outdoors.
Application of LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi in IoT
Approaching a large proportion of IoT use cases, LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi still serve different purposes in IoT. Today Wi-Fi is most often deployed to support critical IoT use cases whereas LoRaWAN is used for massive IoT use cases.
- Massive IoT is applied to connect billions of battery-powered objects, transmit a low amount of data at a low data rate and optimize energy consumption. The application of massive IoT may be found in cities, agriculture, logistics, buildings (airports, hotels, stadiums, multi-dwelling units, homes, venues, etc.), and supply chain or transportation.
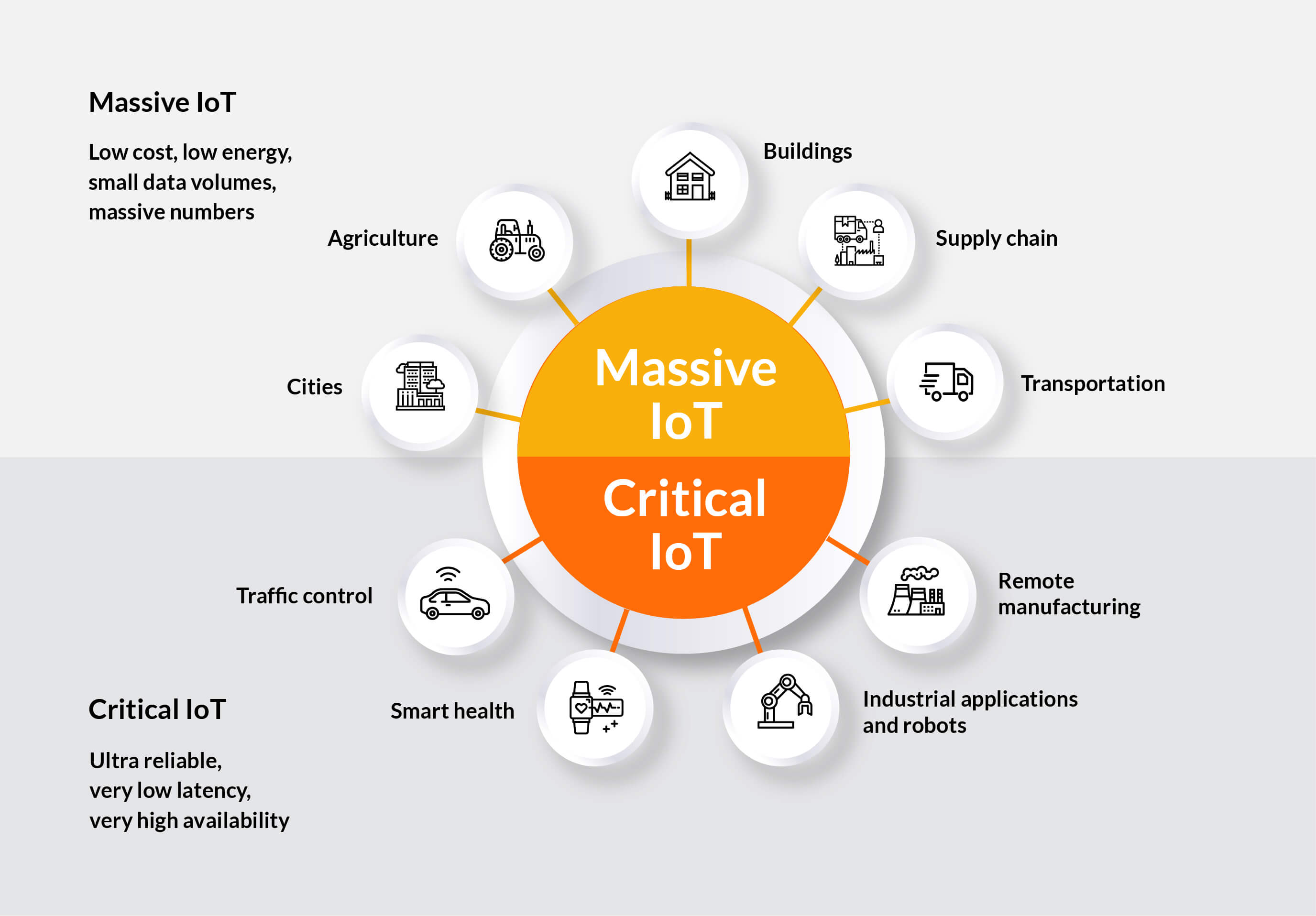
- Critical IoT serves as a connection of millions of objects, communication between a massive amount of data with low latency and high reliability at a higher data rate, which mostly results in higher power consumption. The applications are found in transportation (connected vehicle, traffic control), smart health (surgery, patient monitoring), and industry (real-time applications, robots, remote manufacturing).
Hybrid Wi-Fi/LoRaWAN use cases
For decades, LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi technologies were applied for daily services such as smart buildings, cities, and venues, the same as automotive and smart transportation and location services. The impressive growth of new wireless technologies enabled new commercial use cases in the following commercial sectors.
Smart buildings
In the case of smart buildings, Wi-Fi was commonly used for high-speed Internet surfing, broadband services, and security cameras. LoRaWAN, in contrast, served the leak and smoke detection, air conditioning, door/window opening alarms, asset and vehicle tracking, room energy monitoring and more.
The alliance of these two technologies creates the possibility of on-demand streaming for battery-powered devices. For example, low power LoRaWAN sensors can activate the device that transmits information to the cloud (using Wi-Fi technology) only when it detects sound, motion or vibration in the building. Therefore, the battery of the device will be preserved from unnecessary usage.
Places of residence and venues
Billions of personal and professional devices in homes use Wi-Fi to provide instant connection, whereas LoRaWAN is used for traffic light monitoring, waste management, and traffic direction. It is suggested to use LoRaWAN picos for handling Wi-Fi backhaul portion of the network to the user set-top box to expand coverage of home services to the neighborhood. In such a way, these “neighborhood IoT networks” may endorse the support of new geolocation services and provide the basis for the demand-response services.
Transportation
Currently, Wi-Fi is used for passenger entertainment and access control, while LoRaWAN is used for fleet tracking and vehicle maintenance. Hybrid use cases identified in the paper include location and video streaming. Automotive and smart transportation companies could combine Wi-Fi and LoRaWAN to make location and video streaming more reliable on busses, planes, and other mass transit services.
 AWS IoT
AWS IoT
Just to mention some other peculiarities of LoRaWAN. It is also possible to build well-rounded IoT solutions with transferring data into AWS IoT. Using radio frequency, the gateways have direct access to the LoRa interface of end-devices. Since LoRaWAN devices do not have the AWS IoT SDK installed, security and identification of the network are achieved by the LoRaWAN network. Therefore one may integrate the Network Server with the AWS IoT service to get the data transferred from a LoRaWAN network. Broad and deep functionality, cutting-edge cloud computing for setting up practically any use cases across a large variety of devices and other benefits of AWS IoT make it a best-in-class provider of industrial, consumer, and commercial solutions.
IoT for you
If you found some inspiration while reading about the cases of IoT use cases with LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi connectivity technologies, don’t waste your time and contact Quintagroup to implement your ideas into reality.